Configuration File
Tentris can be configured with a toml configuration file.
This file is conventionally called tentris-server-config.toml.
You can generate a configuration file using the command provided below.
tentris create-default-config
Config File
By default, Tentris will search for a config file in the following directories (in the order they are specified here).
- in the current working directory (
./tentris-server-config.toml) - in the home config directory (
~/.config/tentris-server-config.toml) - in the system config directory (
/etc/tentris-server-config.toml)
If no configuration file is found in any of these directories, Tentris will run in its default configuration (more about that below).
To override which configuration file Tentris uses, use the --config option on the command line as demonstrated below.
# serve with specific configuration
# Note that `--config` comes before `serve`
tentris --config another-tentris-config.toml serve
License File
Unless specified on the commandline or in the config file, Tentris will search for a license file in the following directories (in the order that they are specified here).
- in the current working directory (
./tentris-license.toml) - in the home config directory (
~/.config/tentris-license.toml) - in the system config directory (
/etc/tentris-license.toml)
Example Configuration
Below is an example configuration file. All options have a default value and therefore do not need to be specified. Unless explicitly stated in a comment above the assignments, the assigned values are the default values for their respective options.
# Path to the tentris datastore to open.
# The option set on the command line takes precedence over this value.
# If it is neither set here nor on the command line "./tentris-data" is used.
datastore-path = "./tentris-data"
# Path to the tentris license to use.
# The option set on the command line takes precedence over this value.
# If it is neither set here nor on the command line tentris will search for it in the directories
# listed before this example section.
license-path = "./tentris-license.toml"
[serve]
# The log level
# This can be used as an alternative to the TENTRIS_LOG environment variable
# or the --log-level command line argument.
# The precedence is as follows:
# 1. --log-level argument
# 2. this configuration option
# 3. the TENTRIS_LOG environment variable
#
# Options: "trace", "debug", "info", "warn" or "error"
log-level = "info"
# The format of the log output
# Options: "default" or "json"
log-output-format = "default"
# The address the server should bind to.
# The option set on the command line takes precedence over this value.
bind-address = "0.0.0.0:9080"
# The number of io threads used by the runtime to accept queries/write out results
# Default: number of CPUs in the executing system
io-threads = 8
# The number of threads used by the runtime to evaluate queries
# Default: number of CPUs in the executing system
query-eval-threads = 8
# The chunk size for serialization (4MiB)
query-eval-stream-serialization-chunk-size = 4194304
# The initial chunk size for serialization (1KiB)
query-eval-stream-serialization-chunk-size-start = 1024
# The number of steps to get from query-eval-stream-serialization-chunk-size-start to query-eval-stream-serialization-chunk-size
# The steps are exponential, and for the default configuration (1KiB to 4MiB in 4 steps) the steps are as follows:
# 1KiB, 8KiB, 64KiB, 512KiB, 4MiB
query-eval-stream-serialization-chunk-growth-steps = 4
# Threshold of estimated garbage that needs to be reached in order for the garbage collector to run
garbage-threshold = 1000000
# Disallow running SPARQL updates on the server
# (if true, update endpoints are not available)
read-only = false
# Attempt to automatically repair the datastore after a crash
# The option set on the command line takes precedence over this value
#
# This is equivalent to running tentris repair when it is required.
#
auto-repair = true
# Set the mode for the default graph.
# This is related to https://www.w3.org/TR/2013/REC-sparql11-service-description-20130321/#sd-uniondefaultgraph .
#
# Accepts "standalone" or "union"
# When "standalone" is specified, the default graph is its own distinct graph.
# When "union" is specified, the default graph is the union of all graphs.
default-graph-mode = "standalone"
# Set the default strictness for online updates.
# This setting can be overridden by specifiying the `mode` HTTP query parameter on update routes.
#
# Accepts "strict" or "lax"
# When "strict" is specified, all updates containing invalid statements are rejected.
# When "lax" is specified, the data for `LOAD` and graph-store-protocol queries is allowed to contain invalid statements.
# The invalid statements are discarded, but the rest is inserted.
default-online-update-mode = "strict"
# Limit the number of bytes accepted in request bodies on /sparql, /stream and /update
# Accepts "unlimited" or an integer >= 1.
limit-query-and-update-request-body-size = 8290304
# Limit the number of bytes accepted in request bodies on /graph-store (via POST and PUT)
# Accepts "unlimited" or an integer >= 1.
limit-graph-store-request-body-size = "unlimited"
# Limit the number of bytes the server is allowed to answer on /sparql
# Accepts "unlimited" or an integer >= 1.
limit-sparql-response-body-size = 4294967296
# Timeout in seconds for answering (read) queries
# Accepts "unlimited" or an integer >= 1.
limit-query-duration-secs = 180
# Limit the number of concurrent connection this server will accept (additional requests are rejected if the limit is reached)
# Accepts "unlimited", "auto" or an integer >= 1.
# In case "auto" is specified, will use 2x the number of hardware threads.
limit-concurrent-requests = "auto"
# Limit the number of versions of the triplestore that are allowed to exist in parallel
#
# In write heavy workloads a lower limit results in lower RAM and disk space usage
# whereas a higher limit increases throughput.
#
# For further information see: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Multiversion_concurrency_control
#
# Accepts "unlimited" or an integer >= 2
limit-versions = "unlimited"
# Limit the number of snapshots kept during normal operation
#
# This is primarily useful on filesystems without reflinks (like ext4) because snapshots are a full copy of
# the datastore on these filesystems.
#
# Note: while performing a snapshot this limit will be briefly exceeded by one before the least-recent snapshot is pruned.
# Note: a value of zero indicates that no snapshots will ever be taken automatically. You can still take snapshots via CLI manually.
# Warning: not taking snapshots will render the database unrecoverable in the event of a crash if you have no other snapshots.
#
# Accepts "unlimited" or an integer.
limit-snapshots = 1
# Additional HTML to be placed in the header of the query UI web page
ui-header-html = "<h3>serving your data</h3>"
# TLS/SSL configuration
# By default the server will not use TLS/SSL.
#
# [serve.tls] # comment this line in to enable TLS
#
# Path to TLS certificate PEM file (PKCS#8)
# cert-file = "/path/to/certificate/file"
#
# Path to TLS key PEM file (PKCS#8)
# key-file = "/path/to/key/file"
#
# List of TLS/SSL protocol versions the server will allow
# Accepts list of: "tls12", "tls13"
# acceptable-protocol-versions = ["tls13"]
# Auth configuration
# By default auth will be disabled
#
# [serve.auth] # comment this line in to enable auth
#
# Allow unauthorized access to /sparql, /stream and /ui
# allow-guests = false
#
# Session expiration time in seconds
# A value of 0 indicates that the session should expire when it ends.
# session-expiration-secs = 86400
TLS configuration
To enable TLS, add the [serve.tls] section to the config file.
The cert-file and key-file values are mandatory. acceptable-protocol-versions is optional and will
be set to only include TLS 1.3 by default. An example is shown below:
[serve.tls]
# Mandatory
# Path to TLS certificate PEM file (PKCS#8)
cert-file = "/path/to/certificate-pem-file"
# Mandatory
# Path to TLS key PEM file (PKCS#8)
key-file = "/path/to/private-key-pem-file"
# Optional
# List of TLS/SSL protocol versions the server will allow
# Accepts a list of: "tls12", "tls13"
acceptable-protocol-versions = ["tls13"]
Auth
To enable auth, add the [serve.auth] section to the config file.
All options in this section are optional; the section must simply exist to enable auth.
An example is provided below:
[serve.auth]
# Optional
# Allow unauthorized access to /sparql, /stream and /ui
allow-guests = false
# Optional
# Session expiration time in seconds
# A value of 0 indicates that the session should expire when it ends.
session-expiration-secs = 86400
After auth is enabled, users need to be created and assigned to groups. This process is described in the chapter User Management.
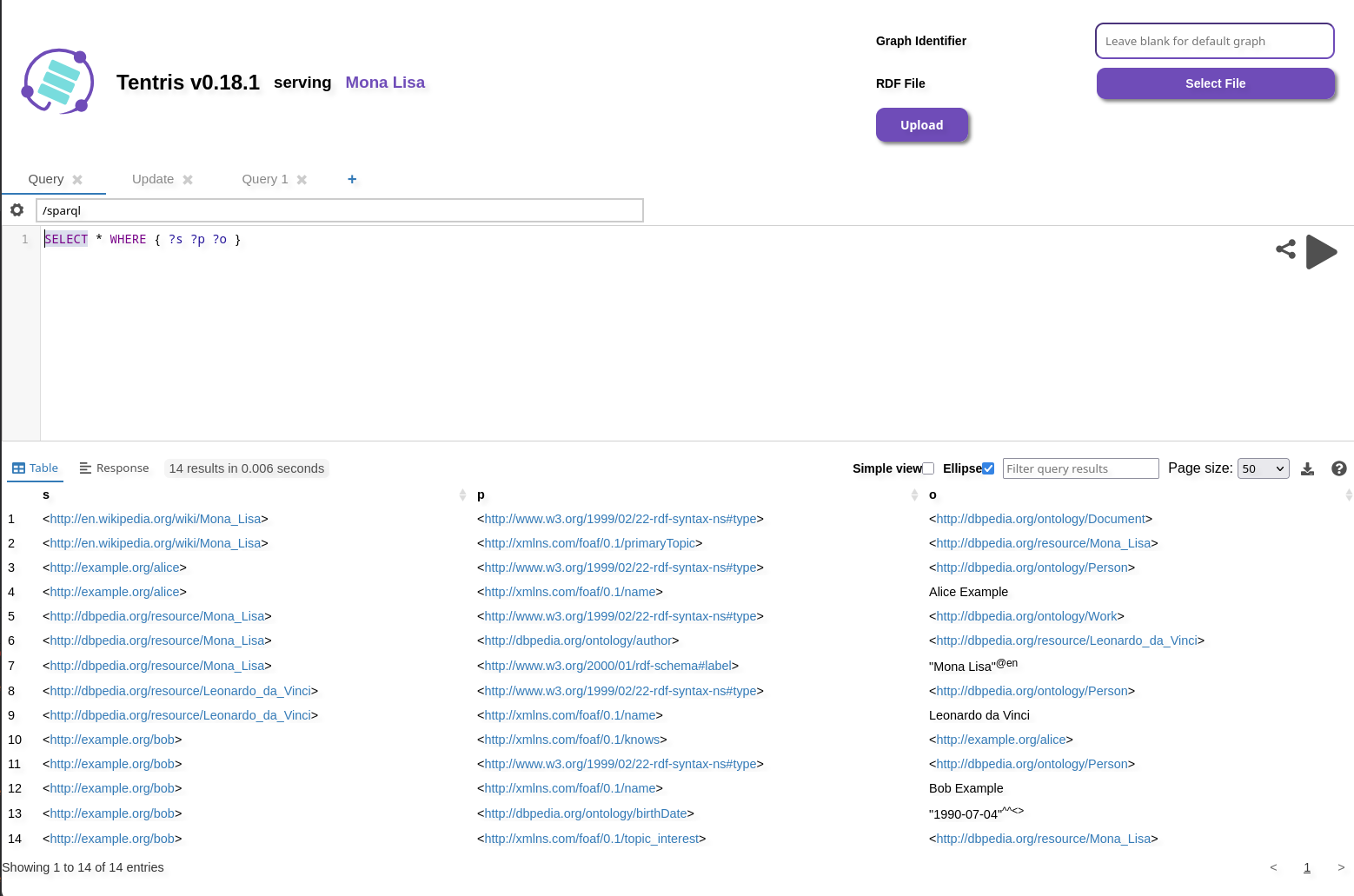
UI Header HTML
To inform users about the dataset a particular endpoint serves, the ui-header-html configuration option may be used.
The HTML text provided to this option is injected into the UI web page, as demonstrated below.
ui-header-html = """
<h3>serving</h3>
<h3 style="color: var(--tentris-purple)">Mona Lisa</h3>
"""
With the configuration from the example above, the UI looks as shown in the following image.